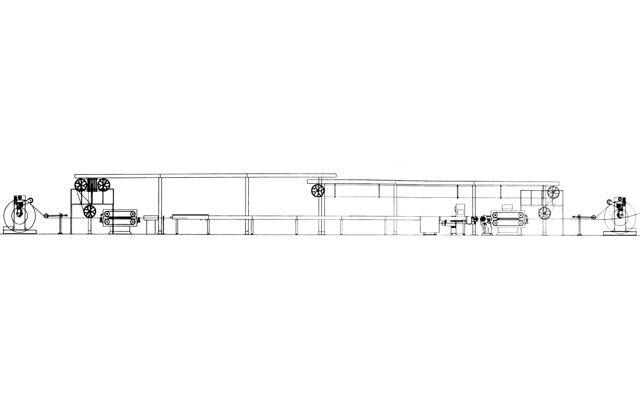
Model 50-150Screw Diameter φ50-150L/D Ratio 26:1/25:1Extrusion Output 70-650 kg/hMain Motor 25-220 KWOutlet Diameter 0.8-120 mmSpeed 10-300Application Power cable
Power Cable Extrusion Line
The power cable extrusion production line is a complete set of equipment that processes solid plastics (such as PVC, PE, XLPE) or rubber materials by heating and pressurizing them into a viscous flow state, then continuously and uniformly coats them onto conductors (e.g., copper or aluminum wires) or cable cores moving at a constant speed. After cooling and solidification, a tight insulating layer or protective sheath is formed.
Power Cable Extrusion Line
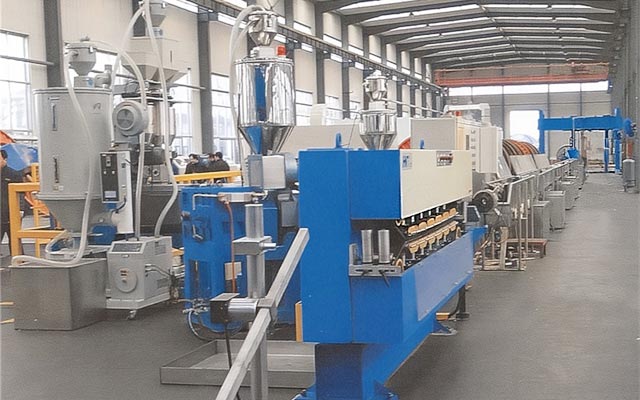
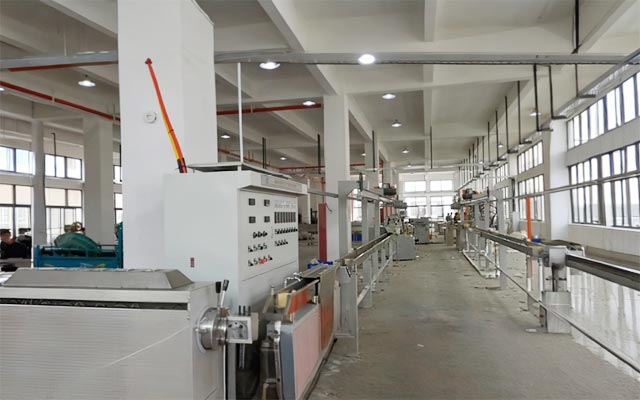
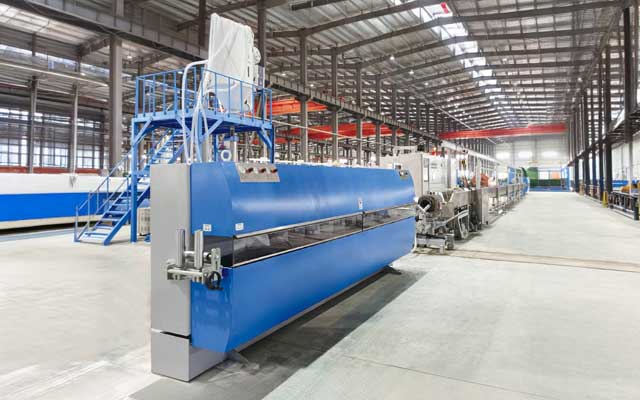



Core Components
A power cable extrusion production line is a highly coordinated automated system, primarily consisting of the following major components:
Pay-off Unit:Supports and releases the conductor or cable core, providing stable and controllable tension to prevent thinning or twisting of the conductor.
Preheater:Heats the conductor before it enters the die head to remove moisture, reduce internal stress, and improve adhesion between the plastic and the conductor.
Extruder:Screw: Conveys, compacts, melts, and homogenizes the plastic.
Barrel: Heats and cools the plastic.
Drive Motor: Provides power to the screw.
Die Head: Connects the extruder to the die.
Die (Tip and Die): Determines the thickness, concentricity, and shape of the extruded layer.
Cooling Trough:Rapidly cools and solidifies the high-temperature cable. Typically features segmented temperature control to ensure material stability and avoid internal stress.
Haul-off Unit:Provides the driving force for the production line. Its speed must be extremely stable, as it is critical for ensuring uniform extrusion thickness.
Spark Tester:An online quality inspection device that applies high voltage to the insulating layer to detect defects such as pinholes or impurities, triggering alarms and marking the locations.
Take-up Unit:Winds the finished cable neatly onto a reel, maintaining constant tension and synchronizing with the haul-off speed.
Control System:Uses a PLC / industrial computer to centrally control all parameters (temperature, speed, tension, etc.), ensuring stable and reproducible production.
Production Line Classification
Extrusion production lines can be categorized in several ways:
By Extrusion Process and MaterialThermoplastic Extrusion Line:
Used for thermoplastics such as PVC and PE. The process is reversible, as the material is simply melted by heating and solidified by cooling. The structure is relatively simple, primarily used for insulating and sheathing low-voltage cables.
Cross-Linking Line:
Used for manufacturing cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulated cables. XLPE transitions from a linear molecular structure to a three-dimensional network through cross-linking, increasing its heat resistance from 70°C to over 90°C and significantly enhancing its mechanical properties. After extrusion, the cable must enter a cross-linking pipe to complete the chemical cross-linking reaction. This is the core equipment for producing medium- and high-voltage cables.
By Number of ExtrudersSingle-Layer Extrusion Line: The most common type, extruding only one material layer at a time (e.g., only insulation or only sheathing).
Dual-Layer Coextrusion Line: Two extruders share one precision die head to simultaneously extrude two different materials. This is mainly used for medium- and high-voltage cables, enabling the simultaneous extrusion of conductor shielding and insulation layers or insulation and insulation shielding layers. Coextrusion ensures a smooth interface, no contamination, and strong bonding.
By Product StructureInsulated Core Extrusion Line: Used for extruding insulation onto conductors.
Cable Sheathing Extrusion Line: Used for extruding outer sheathing onto cable cores.
Sector Conductor Insulation Extrusion Line: Specifically designed for extruding insulation onto sector-shaped conductors.
Power Cable Extrusion Line Datasheet
| Model |
50 |
70 |
80 |
90 |
100 |
120 |
150 |
| Screw Diameter (mm) |
φ50 |
φ70 |
φ80 |
φ90 |
φ100 |
φ120 |
φ150 |
| Screw L/D Ratio |
26:1 |
26:1 |
26:1 |
26:1 |
25:1 |
25:1 |
25:1 |
| Extrusion Amount (kg/hr) |
70 |
140 |
200 |
250 |
320 |
450 |
650 |
| Outlet Wire (mm) |
0.8-5 |
2-15 |
3-25 |
5-35 |
8-60 |
10-80 |
15-120 |
| Total Power (KW) |
25 |
40 |
55 |
63 |
120 |
165 |
220 |
| Production Speed(Max., m/min) |
300 |
300 |
200 |
200 |
100 |
80 |
60 |
| Take-up Spool |
400/630 |
500/800 |
800/1250 |
800/1600 |
1000/2000 |
2000/2500 |
2500/3150 |
| Storage Length |
240 m |
240 m |
200 m |
180 m |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Power Cable Extrusion Line Application
The power cable extrusion production line is a complete set of equipment that processes solid plastics (such as PVC, PE, or XLPE) or rubber materials by heating and pressurizing them into a viscous flow state, then continuously and uniformly coats them onto conductors (e.g., copper or aluminum wires) or cable cores moving at a constant speed. After cooling and solidification, a tight insulating layer or protective sheath is formed. In power cable manufacturing, it is primarily used in the following three processes:
Conductor Insulation
Function: Extrudes insulating material onto copper or aluminum conductors to form the primary insulation layer.
Common Materials: Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), etc.
Requirements: Uniform thickness, high concentricity, absence of impurities, and no microvoids. The insulation extrusion process for high-voltage cables demands the highest technical precision.
Sheathing Extrusion
Function: Extrudes a protective sheath over the assembled cable core.
Purpose: Provides mechanical protection, corrosion resistance, moisture resistance, UV resistance, flame retardancy, etc.
Common Materials: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE), polyolefins, etc.
Shielding Layer/Liner Layer Extrusion
Function: Extrudes semiconductive shielding layers (conductor shielding and insulation shielding) for medium- and high-voltage cables to evenly distribute the electric field. Sometimes also used for extruding liner layers to fill gaps within the cable core.